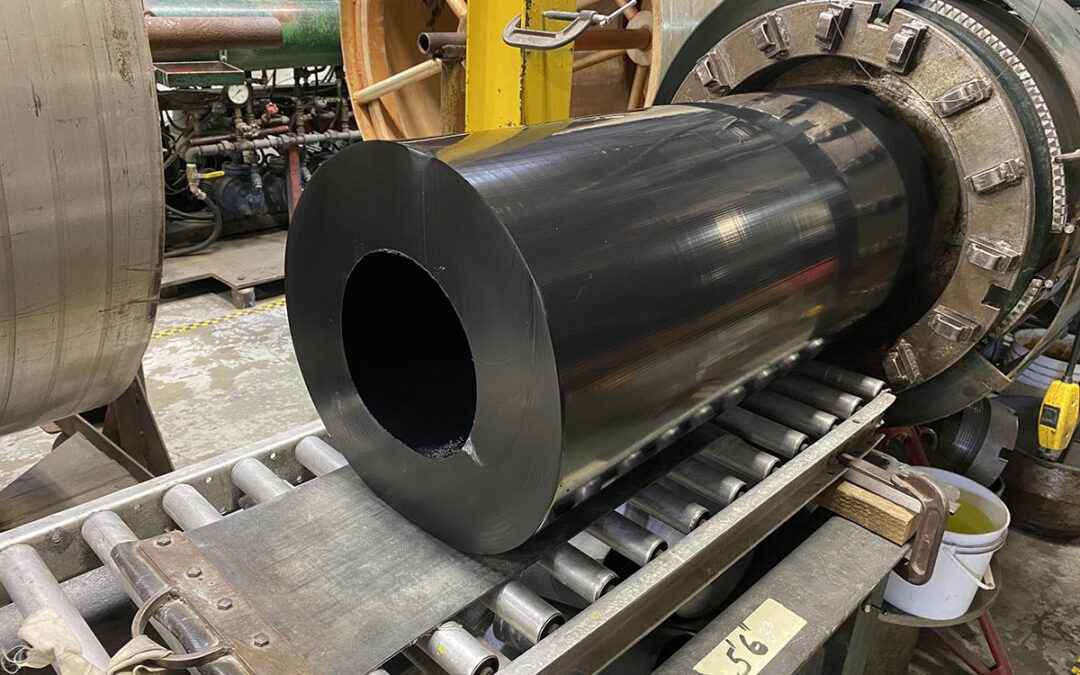
What are Rubber Extruded Products?
Rubber extruded products are highly popular due to their balance between high build quality and relative ease of production. Rubber extruded products are durable, long-lasting, flexible, and highly resistant to many different effects including chemicals, high temperatures, low temperatures, impacts, and abrasion. Along with these benefits for the customer, the rubber extrusion process is beneficial to manufacturers as well thanks to its economical cost and minimal product waste from start to finish.
Extruded rubber is a collection of products introduced in the 1930s that are created by forcing elastomeric compounds to flow through a hard surface known as a die. Extruded rubber products are built from many different cross-sections, from simple solid profiles such as squares and rectangles, to hollow profiles that facilitate sealing such as U-Channels and D-Fenders. Extruded rubber can be softened and pressurized into thousands of unique profiles based on the shape of the die, allowing it to be used in industries ranging from aerospace, construction, consumer goods and more.
Rubber Extrusion Process
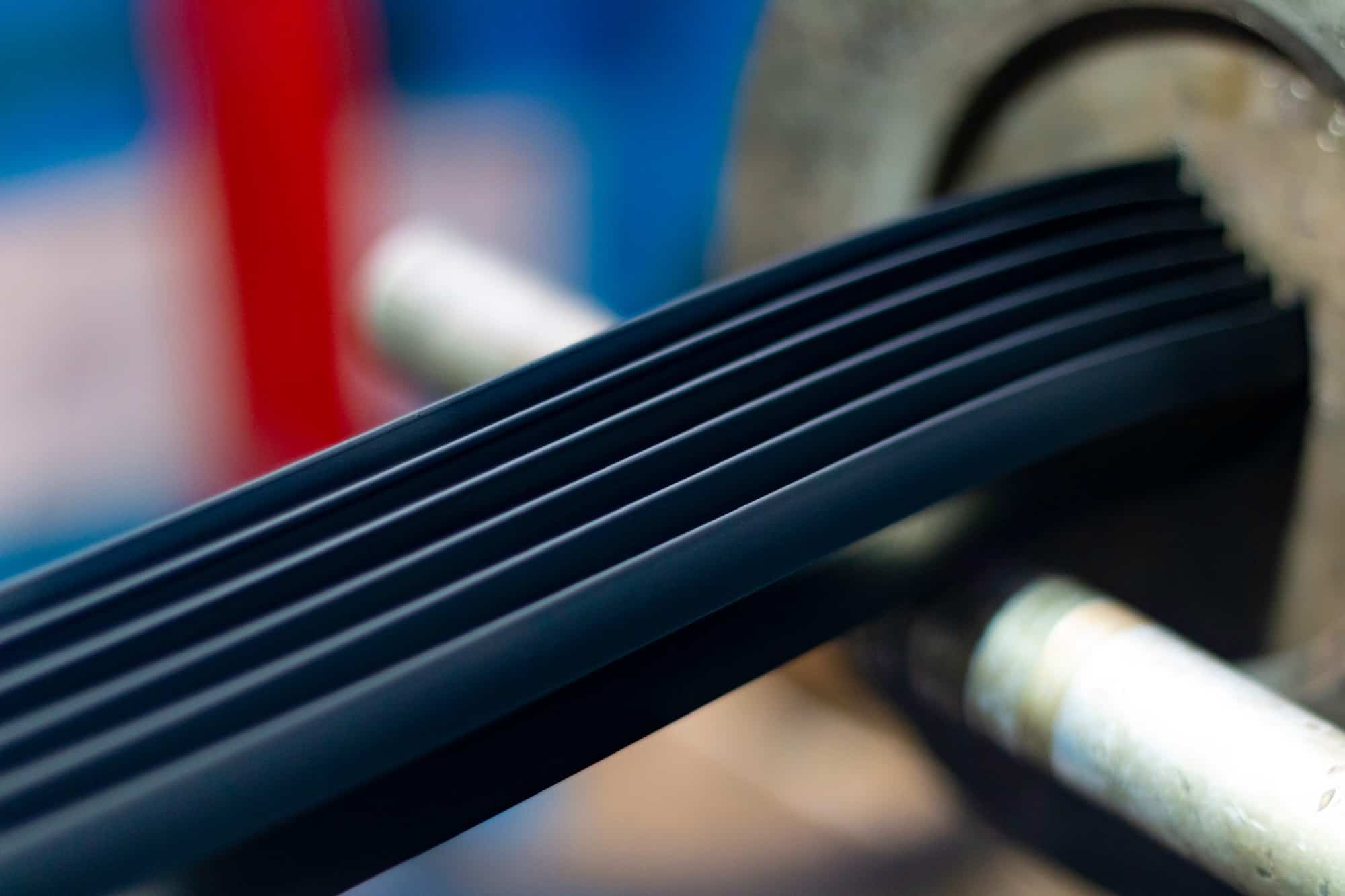

Collection of Raw Materials
The rubber extrusion process begins with the collection of raw materials. These materials are precisely selected to achieve specific properties such as elasticity, hardness, and resistances to various phenomena. The material of choice and its properties is entirely dependent on the task at hand, as well as the goal the product serves.
Feeding the Extruder
Following the selection of the raw material, the extruder is fed into the hopper, a tool that applies enough heat and pressure to convert the raw material into a flowing mass that can be easily shaped.
Shaping through the Die
Next, the processed materials are fed through a die built to meet the specifications of the product. This die shape can range from a simple seal to a highly elaborate gasket. As the rubber material moves through the die, it is cooled and then cured, cut, and spooled as required. This process is highly versatile and can be adjusted in many ways to create a wide range of products with their own unique shapes, requirements, and compositions.
Common Rubber Extrusion Products
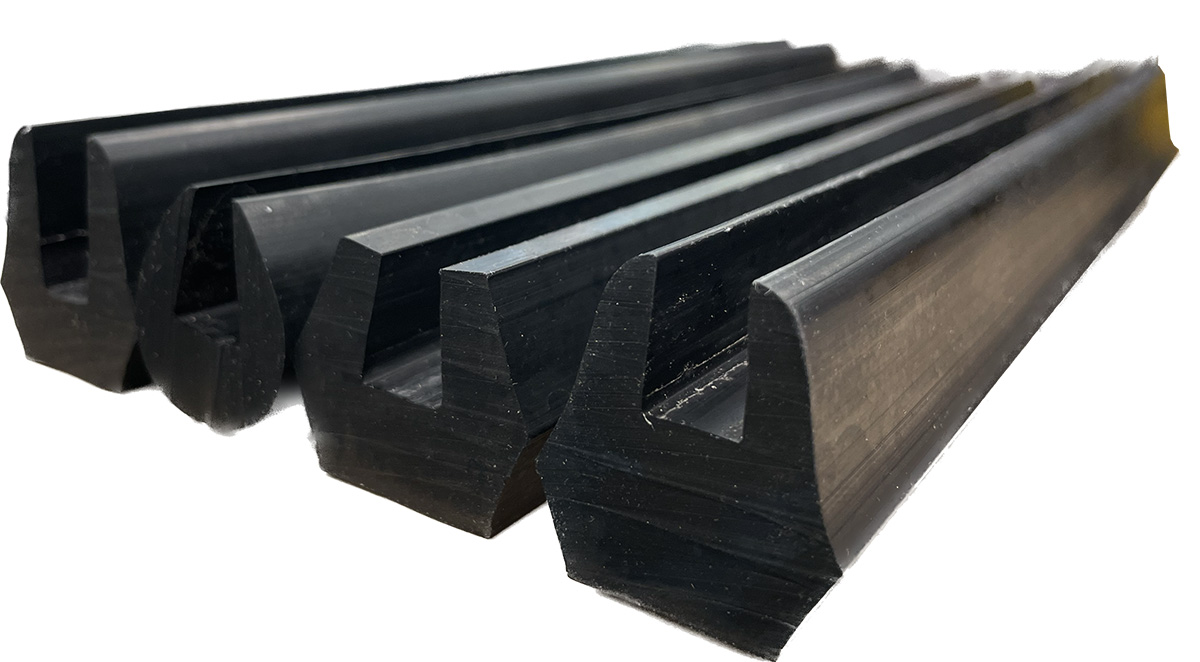
As extruded rubber is used in the majority of industrial applications, there are a wide variety of extruded rubber products that provide a key service to many industries. Below are some examples of common products manufactured through the rubber extrusion process:
- Rubber Gaskets & Seals: Manufactured for weatherproofing vehicles, shelters and equipment. Special care is given to ensure materials that are chemical and heat resistant are used in the extrusion process.

- Rubber Bumpers: Manufactured to protect trailer truck docks, boat fenders and other heavy equipment from shocks and impacts.
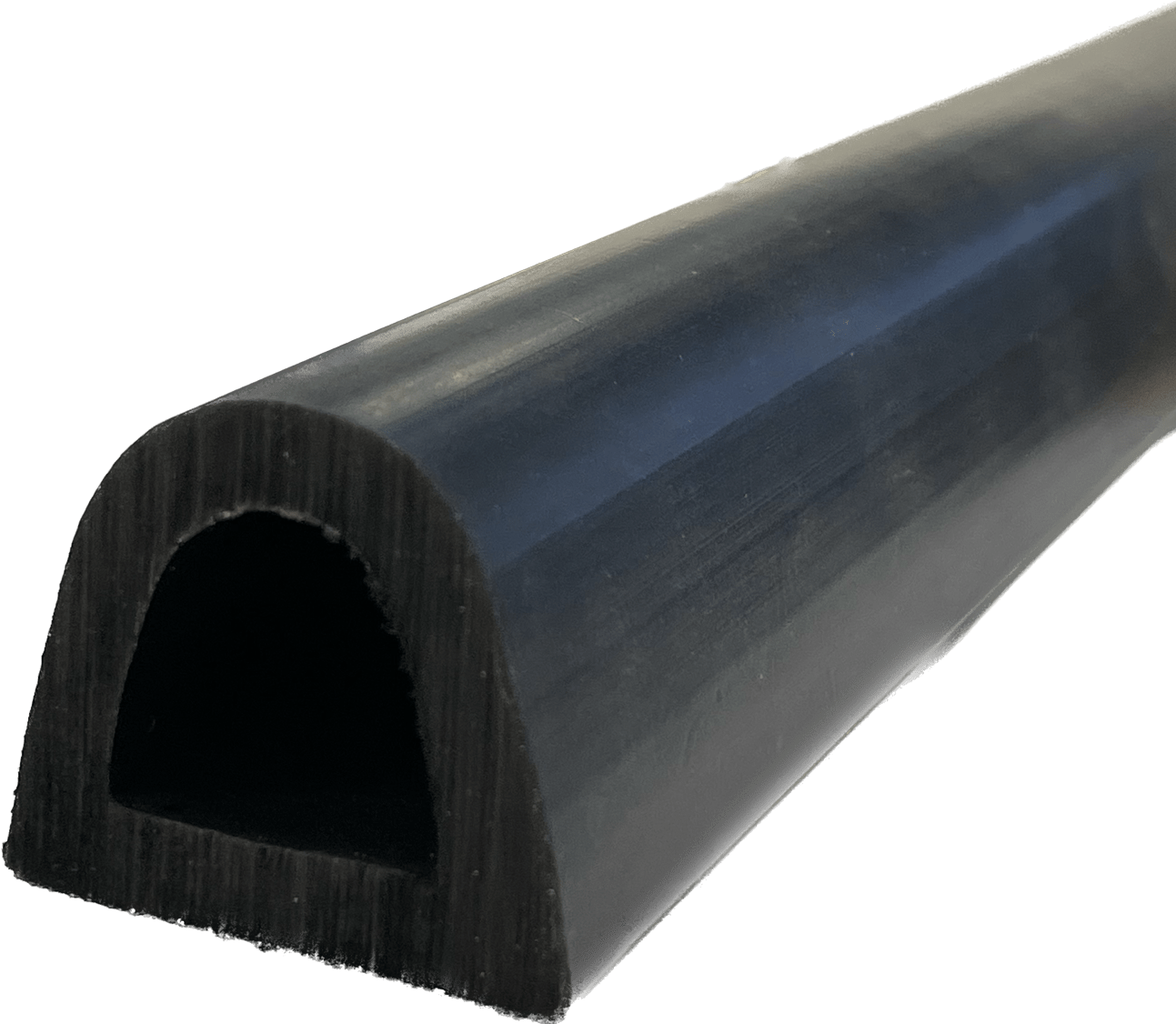
- Rubber Bushings: Manufactured to isolate moving parts and prevent vibrations and noises. Commonly used as shock absorbers for automotive systems, particularly in suspensions. Rubber bushings can be bare rubber only or enclosed in metal sleeves.

- Rubber trims: Manufactured to provide an air-tight seal between parts, as well as protect edges and surfaces from impact. Commonly used for windows, doors, and hatches.

- Rubber Weatherstrips: Used more commonly in automotive and building construction. Manufactured to isolate rooms from external elements such as extreme weather, pollution, and water. Highly elastic and capable of resisting vibrations without sacrificing its tight seal.
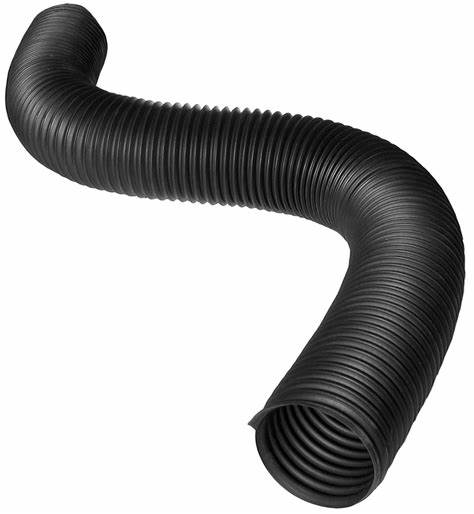
- Rubber Tubing and Hoses: Rubber’s excellent flexibility permits it to be bent into shape without damage, making it a perfect material to transfer various fluids such as compressed air, water, and chemicals.

12 Common Rubber Extrusion Materials

Despite being a highly versatile process, the materials used in rubber extrusion must be selected mindfully in order to create a capable and reliable product. There are a wide variety of extrusion materials to select from, each offering their own unique chemical resistances, degradation resistance, mechanical properties, general elasticity, insulation, shock absorption, and price. Listed below are 12 types of rubber commonly used in the rubber extrusion process, along with their strengths, weaknesses, and best uses:
Natural Butadiene (NBR) Rubber
NBR accounts for roughly a quarter of the entire world’s production of synthetic rubber. It is mainly used in the production of tires, but it can also improve product properties as part of a blend of materials. NBR possesses strong resistances to cracks, abrasion, and rolling, however it is susceptible to ozone degradation.
Styrene-Butadiene (SBR) Rubber
SBR is the result of copolymerization between styrene and butadiene. Not only is SBR crucial in the production of extruded rubber parts, but it is also vital for many extremely common items including tires, gaskets, and shoes.
SBR’s strength lies in its jack-of-all-trades, general purpose qualities, making it a strong competitor with natural rubber in terms of market share. It is a sought-after material due to its superior abrasion, tear, and thermal resistances compared to natural rubber.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene (Nitrile) Rubber
Nitrile rubber is produced from the copolymerization of acrylonitrile and butadiene. Nitrile rubber is most common in the automotive industry due to its natural resistances to petroleum-based chemicals such as oils, fuels, and grease. While they are excellent gaskets and sealants, nitrile rubber is not well-equipped for tough environments due to its low tensile strength and inability to handle low temperatures. While these problems can be mitigated by compounding reinforcing fillers, be wary of nitrile rubber’s limitations.
Ethylene Propylene Dieme (EPDM)
EPDM is made from the copolymerization of ethylene and propylene, along with the optional addition of diene for curing. This material boasts strong weathering resistance and good insulating properties regardless of the inclusion of diene. In addition, EPDM can stand up to both high and low temperatures, maintaining its excellent mechanical properties and chemical resistance. Along with nitrile rubber, EPDM is the material of choice for automotive sealing.
Butyl Rubber
Butyl Rubber is a copolymer of isobutylene and isoprene. One of butyl rubber’s defining characteristics is its low unsaturation, allowing it to repel most gas and liquid chemicals. Additionally, vulcanized butyl rubber is highly durable and resistant to aging. This combination of chemical repelling qualities and aging resistance makes butyl rubber a popular material for gaskets, trims, hoses, and O-rings.
Halogenated Butyl (Halobutyl) Rubber
Butyl rubber can be modified to halobutyl rubber by reacting allylic chlorine and bromine. While this method can help improve ozone and chemical resistance, it comes at the cost of traditional butyl rubber’s insulation capabilities and water resistance. Halobutyl rubber is characterized by its low permeability to moisture and gas relative to other rubber types and a similar breadth of applications as traditional butyl rubber.
Chloroprene (Neoprene) Rubber
Chloroprene was one of the first synthetic rubbers ever produced when it was developed by DuPont in 1930. Boasting a higher aging resistance and durability than natural rubber, it became a highly popular material during the rubber shortages of World War 2. While much more expensive than natural rubber due to its compounding additives, its inherent chemical inertness makes it a strong choice for weatherstripping seals, gaskets, and hoses.
Fluorocarbon (Viton) Rubber
FKM rubbers are produced from the copolymerization of vinylidene fluoride with various chemicals including hexafluoropropylene and tetrafluoroethylene. FKM’s greatest strength lies in its high resistance to virtually all chemicals as well as its good mechanical properties. This combination makes FKM very popular in the production of cord stocks for O-rings and other sealing products.
Natural (NR) Rubber
Simple and effective, NR is the tried-and-true material in rubber extrusion thanks to its excellent heat buildup and fatigue resistance compared with other rubbers.
Isoprene Rubber
In terms of polymer chain structure, isoprene rubber holds many structural similarities to natural rubber. Isoprene rubber is a widely-used, general-purpose rubber that possesses similar heat buildup, fatigue resistance and impact absorption as natural rubber. Isoprene rubber is popular in the production of shock absorbers and rubber bushings thanks to these characteristics.
Silicone Rubber
Silicone rubber is unique from all other rubbers due to its lack of a carbon-based polymer backbone. Instead, silicone rubbers are built from a silicon-oxygen chain that is bonded to various functional groups including vinyl and phenyl. Silicone rubber is decently resistant to oxygen, ozone, heat, light, and moisture. However, silicone rubber suffers from weak mechanical properties and are far more expensive to produce. In part to its wide variety of resistances, silicone rubber is useful in many industrial applications, with a focus on food and drug manufacturing.
Polyurethane Rubber
Polyurethane rubber is highly versatile due to its ability to be formulated in various ways in order to achieve the properties that best suit the application at hand. Manufacturers can achieve specific hardness, compression set, tensile strength, and resistances by combining different types and quantities of compounding ingredients,. Polyurethane rubber’s design flexibility of both plastics and rubbers makes it a popular choice in the production of shock absorbers, dampers, protective sleeves, trims, and bushings.
Redwood Plastics & Rubber’s diverse extrusion capabilities enable us to provide both traditional and custom extrusions for a wide range of industries. To learn more about our rubber extrusion capabilities, click the button below.

